1.输入数据
选择列式表格和列式散点图。如果您还没有准备好输入自己的数据,可以从欢迎对话框中选择列式表样本数据 "频率分布"。
2.选择分析
单击分析,然后从列数据分析列表中选择频率分布。
3.选择分析选项
累积?
在频率分布中,每个二进制数值包含在定义该二进制数值范围内的数值个数。在累积 分布中,每个二进制数都包含该二进制内或该二进制以下的数值个数。根据定义,最后一个 bin 包含数值总数。下图左侧是频率分布图,右侧是相同数据的累积分布图,两者都绘制了每个 bin 中的数值个数。
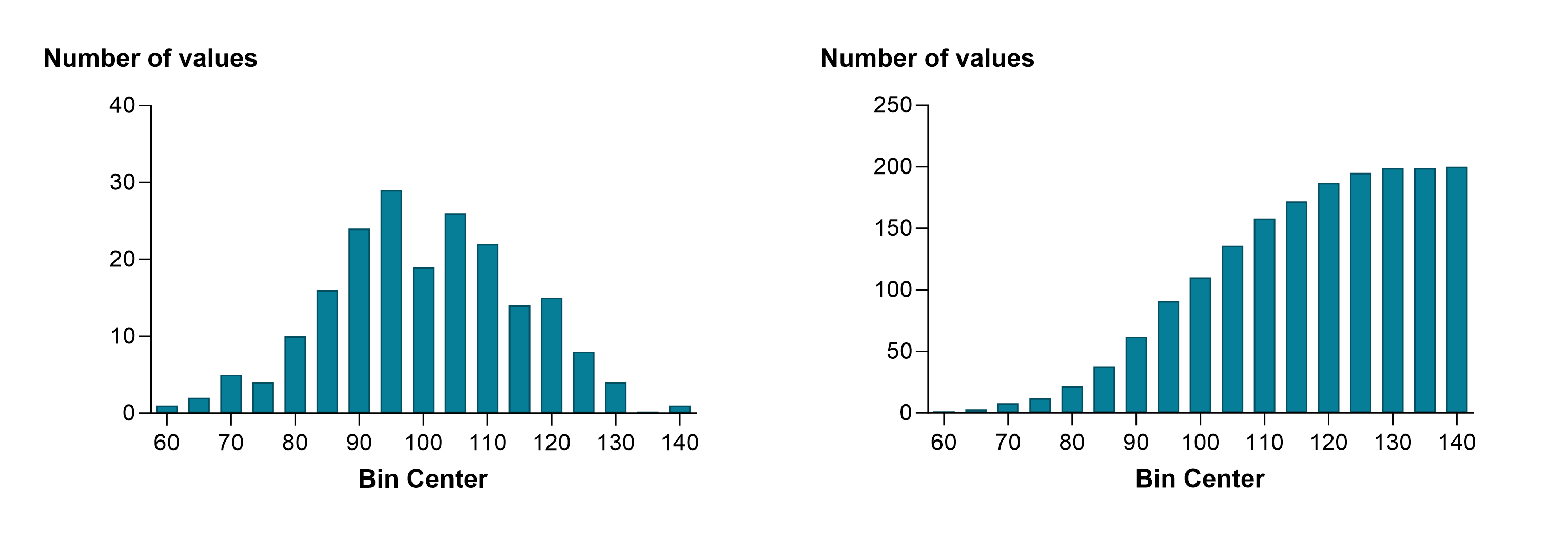
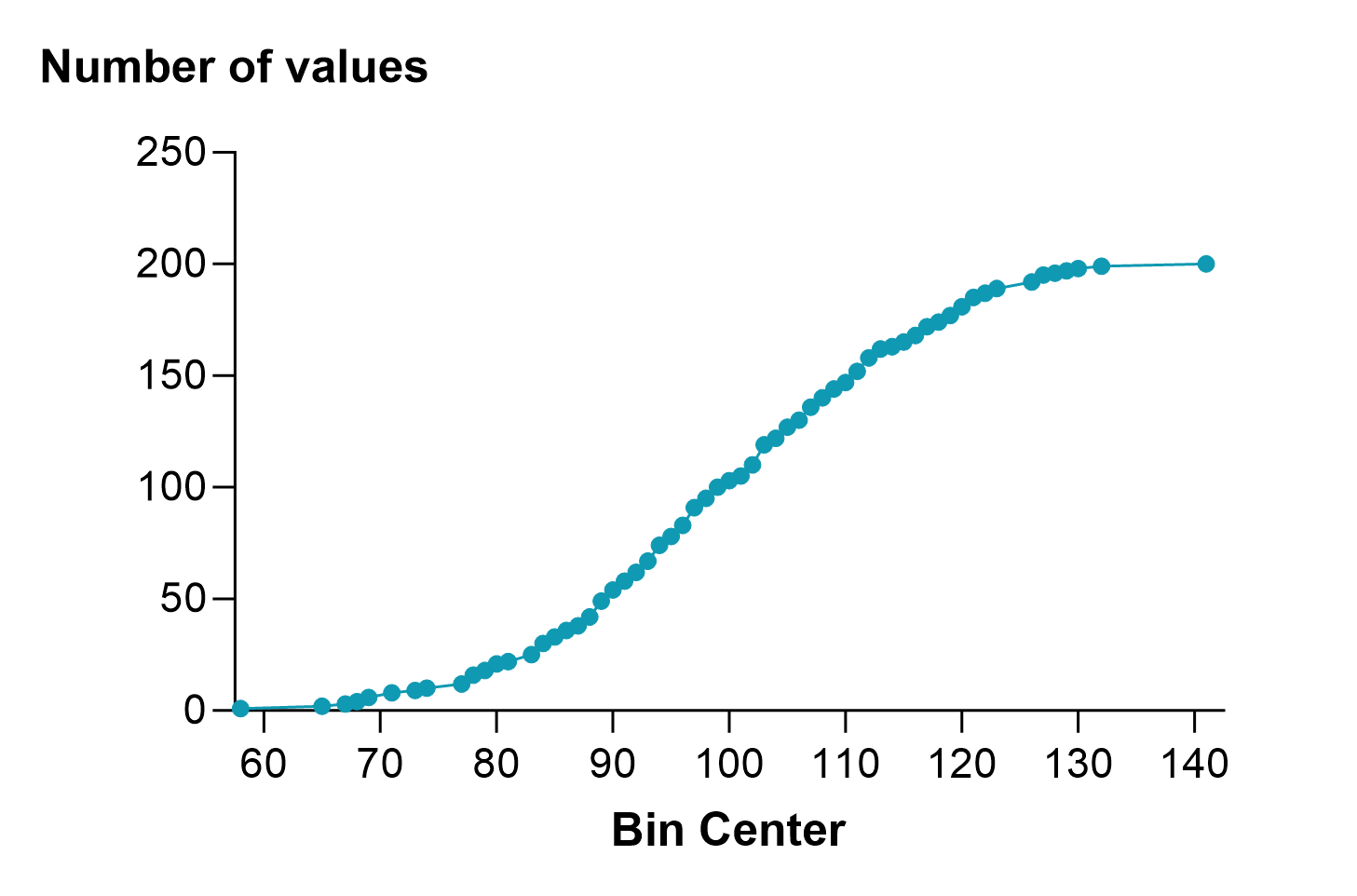
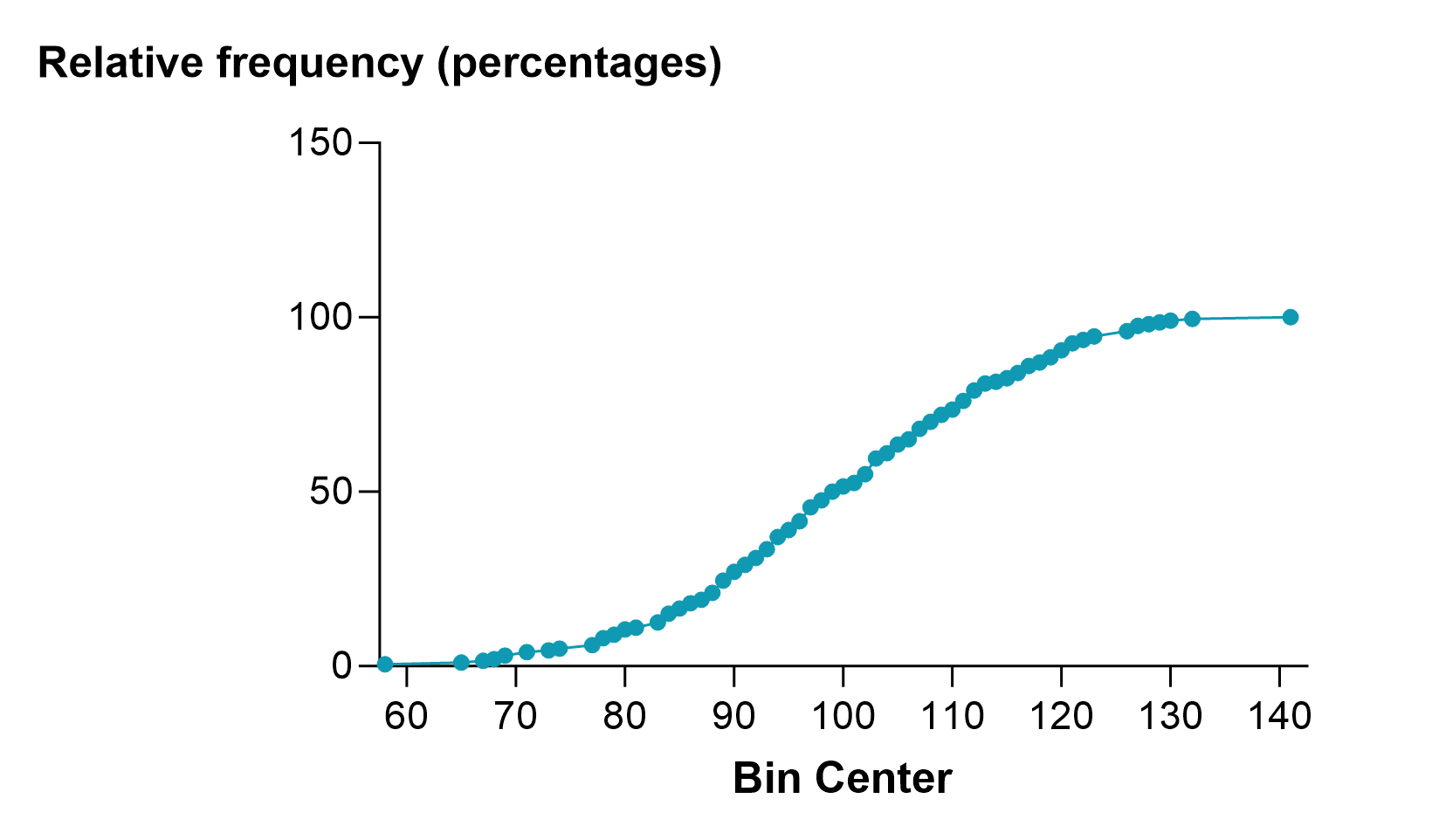
累积分布的主要优点是不需要确定箱宽。相反,您可以将精确的累积分布制成表格,如下左图所示。这个数据集有 200 个值,因此这个精确的累积分布有 200 个点,使其有点粗糙。当您选择将累积频率分布以百分比而不是分数或精确计数的形式制表时,这些百分比实际上就是百分位数,所得到的图形有时也称为百分位数图(如下右图所示)。
相对频率或绝对频率?
选择 "相对频率 "来确定每个分区中数值的分数(或百分比),而不是每个分区中实际值的数量。本示例中,如果 45 个值中有 15 个属于某个分区,则相对频率为 0.33 或 33%。
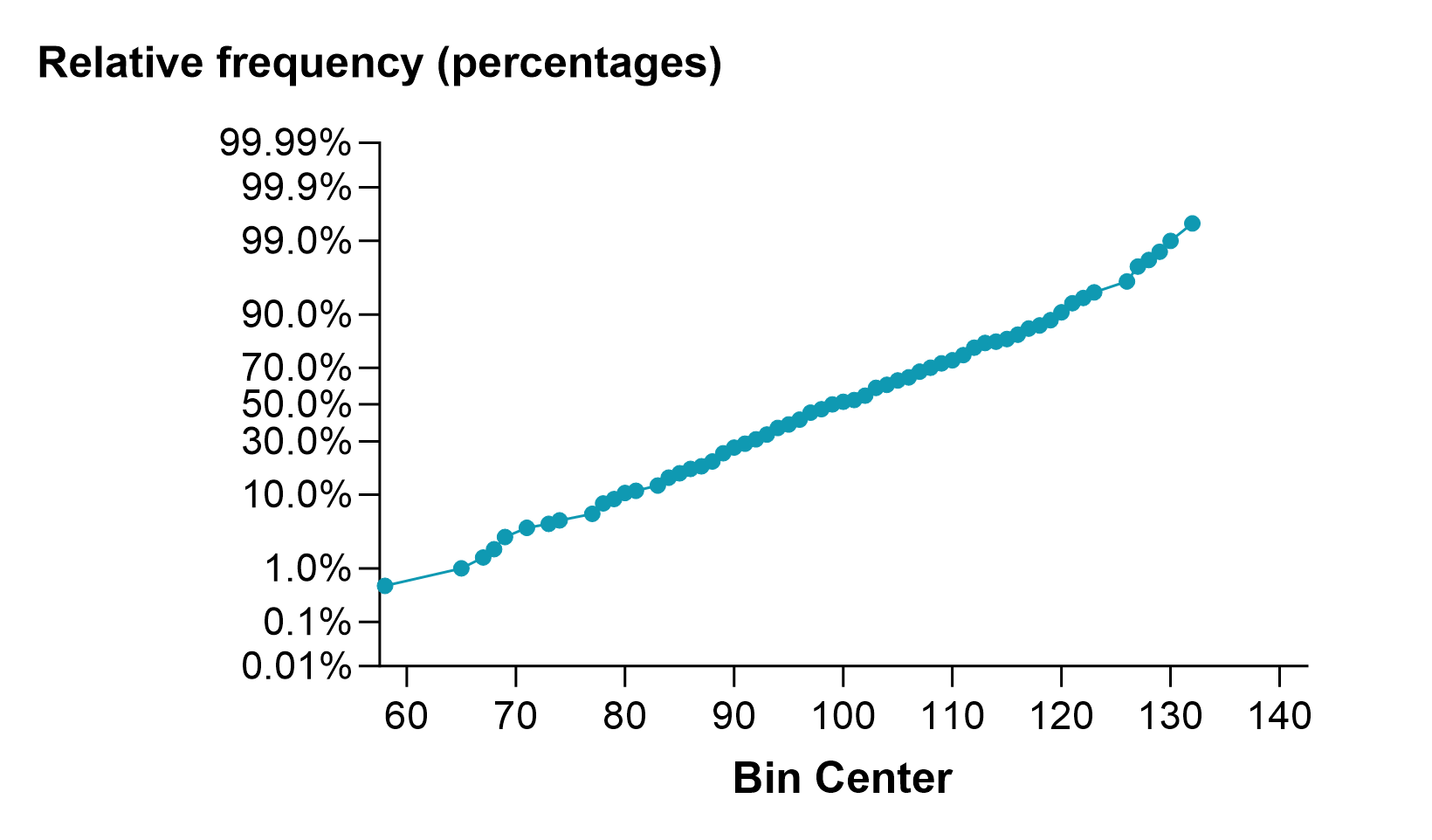
如果同时选择累积频率和相对频率,就可以使用概率轴来绘制分布图。以这种方式绘制时,高斯分布是线性的。下面是一个使用与之前相同数据的本示例。在这种情况下,数据大致遵循正态分布,因此图形基本上是一条直线。
Bin width
If you chose a cumulative frequency distributions, we suggest that you choose to create an exact distribution. In this case, you don't choose a bin width as each value is plotted individually.
To create an ordinary frequency distribution, you must decide on a bin width. If the bin width is too large, there will only be a few bins, so you will not get a good sense of how the values distribute. If the bin width is too low, many bins might have only a few values (or none) and so the number of values in adjacent bins can randomly fluctuate so much that you will not get a sense of how the data are distributed.
How many bins do you need? Partly it depends on your goals. And partly it depends on sample size. If you have a large sample, you can have more bins and still have a smooth frequency distribution. One rule of thumb is aim for a number of bins equal to the log base 2 of sample size. Prism uses this as one of its two goals when it generates an automatic bin width (the other goal is to make the bin width be a round number).
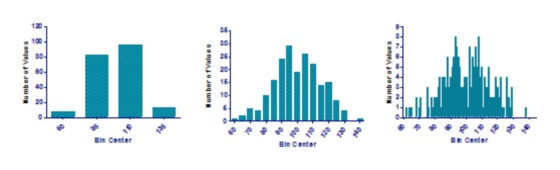
The figures below show the same data with three different bin widths. The graph in the middle displays the distribution of the data. The one on the left has too little detail, while the one on the right has too much detail.
料仓范围
除了决定控制箱数的箱宽之外,还可以选择第一个箱的中心。这一点可能很重要。想象一下,您的数据是百分比,从 0 到 100。不可能出现小于 0(负值)或大于 100 的值。比方说,您希望箱宽为 10,这样就有 10 个仓。如果第一个二进制以 0 为中心,它将包含 -5 和 5 之间的值,下一个二进制将包含 5 和 15 之间的值,下一个二进制将包含 15 和 25 之间的值,等等。由于不可能出现负值,因此第一个箱宽实际上只包含 0 到 5 之间的值,所以它的实际箱宽是其他箱宽的一半。还要注意的是,有 11 个二进制包含数据,而不是 10 个。
如果将第一个二进制以 5 为中心,它将包含 0 到 10 之间的值,下一个二进制包含 10 到 20 之间的值,等等。现在,所有二进制都真正包含了相同范围的值,所有数据都包含在十个二进制中。
边界上的一个点与包含较大数值的 bin 相一致。因此,如果一个 bin 从 3.5 到 4.5,而下一个 bin 从 4.5 到 5.5,那么 4.5 的值就会进入第二个 bin(从 4.5 到 5.5)。
副本
如果输入了重复值,Prism 可以将每个重复值放入相应的分选箱中,或者将重复值取平均值,只将 平均值放入分选箱中。
所有太小而无法拟合到第一个二进制中的值都会从分析中省略。您还可以输入一个上限,以便在分析中忽略较大的值。
如何绘图
请参阅本示例。
|
Prism 只能对数值数据进行频率分布。它可以处理分类数据,但前提是必须将分类作为值输入。 |
